User Guide
Calculating an intra-series standard deviation
When measuring the variability of a process from a series of samples of several parts, two types of variability can be distinguished:

If we mix all the parts and calculate the standard deviation of the overall sample, we will calculate the overall standard deviation of all the parts. This standard deviation takes into account all the variation in the sample, including the variation between samples.
However, it is sometimes necessary to separate the variability between the intra-sample variability and the variability between samples.
This is the case, for example, when we want to calculate a short-term capability from several samples. The intra-sample variability then represents the intrinsic variability of the production machine, while the global variability also takes into account the machine's deviations over a longer time.
This is also the case when one wants to calculate the dispersion of a measuring instrument during an R&R study. The intra-sample variability then represents the repeatability (or reproducibility depending on the sampling) of the measurement process, while the overall variability also takes into account the part variability.
To calculate the intra-sample standard deviation, there are two methods of calculation:
Range method: Very easy to use, calculations can be done by hand, it requires however to have only samples of the same size.
Variance method: The calculations are more complicated, but very easily done by a computer. This method can be used when the samples are not the same size.
Range method :
To calculate the intra-sample standard deviation from the Range method, it is necessary to calculate a series of samples of the same size as in the following example

For each sample, we calculate the range R.
Then we calculate the average of the ranges, in the previous example:
The intra-sample standard deviation is simply calculated by the formula
d2 is a coefficient that can be deduced from the following table. It depends on the number of subgroups used for the calculation, as well as the number of measurements in each subgroup.
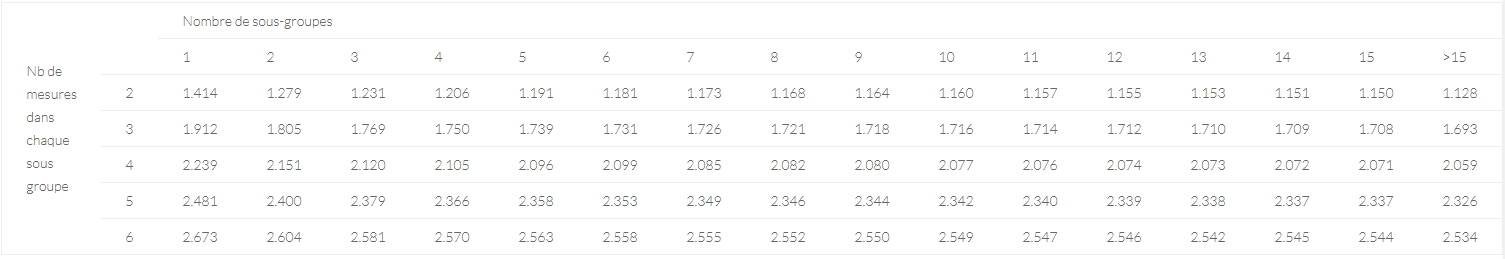
In the previous example, we had 5 subgroups of 3 pieces, so we deduce
As a result :
Method from the variance:
To calculate the intra-sample standard deviation from the Range method, it is not necessary to have a series of samples of the same size, it is simply necessary to have a series of samples of more than 2 pieces each, as in the following example:
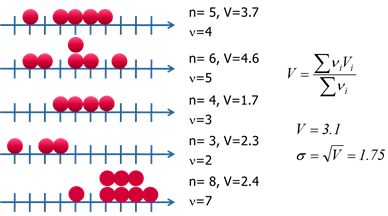
For each sample, we compute :
- ni: Number of pieces constituting the sample
- vi: Number of degrees of freedom of the sample = n-1
- Vi: Variance of the sample : The calculation of the within-sample variance is done by :
We then deduce the calculation of the intra-sample standard deviation: